Lecithin is a mixture of phospholipids, glycolipids, glycerides, and other minor components. It is to this high phospholipids content that lecithin owes specific functions. Phospholipids are amphiphilic, i.e. they have different affinities for oil and water. Lecithin forms stable O/W and W/O emulsions and durable dispersions in a wide range of applications.
It is generally found in all living cells as a major component of the cell membrane, which regulates the nutrients entering and exiting the cell or the metabolic processes. Lecithin is a vital feature of all life, it is an essential nutritional supplement.
Vegetable origin lecithin is derived during stages of oil refining of soya, sunflower, rapeseed, or rice bran oil.


One of the ways is by HLB (Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance).
Different Emulsifiers have different HLB values and depending on the composition of the proposed emulsion, proper emulsifiers are selected.
HLB stands for Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance. Low HLB Value is more lipophilic or they have more affinity towards lipids (oil). A high HLB value shows more affinity towards water. Emulsifiers with high HLB values are used in O/W type of emulsions and vice versa.
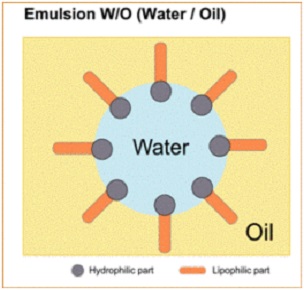
Water in Oil. Butte, Margarines, oil is in continuous form while water is dispersed in small droplets.
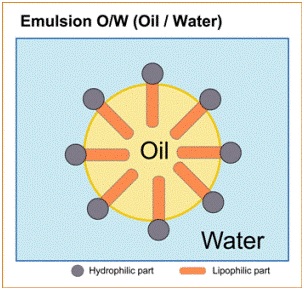
Oil in Water e.g. Milk, cream (buttercream). Milk and milk fat -water is the continuous phase and fat is in suspended form.
Emulsifiers are molecules having groups with water & oil solubility or affinity. For e.g. Lecithin fatty acid chains have an affinity for oil & phosphatide chains have an affinity for water due to their polarity. Thus this molecule can hold together both oil and water.
© 2022 GIIAVA. All Rights Reserved. Developed by Quantazone